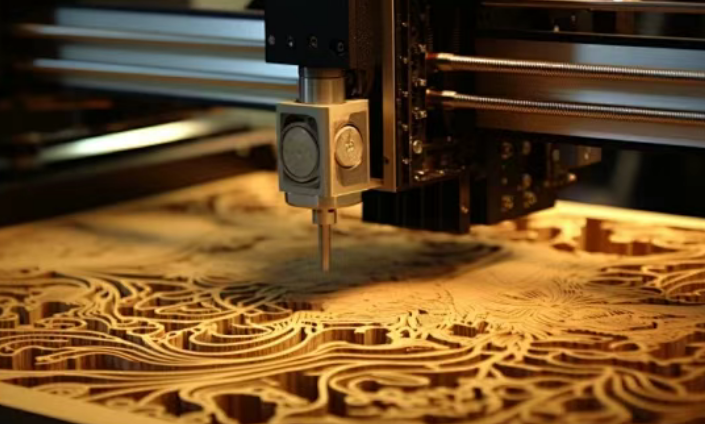

Laser engraving is a familiar process to many people. It is based on CNC (computer numerical control) technology and uses laser as the processing medium. During laser engraving, the focused laser beam melts or vaporizes the material instantly, creating physical changes on the surface. This enables precise and permanent marking or engraving without damaging the material.
Laser engraving is widely applied to various materials, and the engraved patterns or text remain smooth and wear-resistant since no mechanical contact is involved.
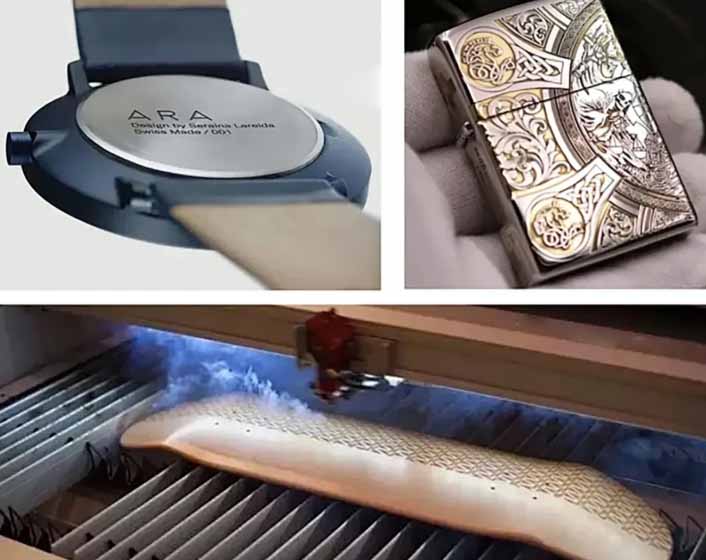
Examples of Laser Engraving Applications:
Leather Processing Industry

Advertising and Sign-Making Industry

Advantages of Laser Engraving
High Precision:
Laser engraving can reach micrometer-level accuracy, ensuring almost zero errors during processing.Non-Contact Process:
Since the laser beam doesn’t physically touch the material, no mechanical stress or deformation occurs, preserving the quality of the workpiece.High Speed and Efficiency:
Laser engraving operates very quickly — suitable for large-scale or batch production.Flexible Design Changes:
Engraving patterns can be switched instantly by simply loading a new design file, which makes it ideal for customized production.Wide Material Compatibility:
Laser engraving can be applied to many types of materials, though results may vary depending on surface texture or composition.
Limitations of Laser Engraving
Maintenance Cost:
Large industrial laser systems can have high maintenance costs. However, small and desktop laser engravers generally require less upkeep.Material Limitations:
Not all materials are suitable for laser engraving; some may produce unsatisfactory results or even release harmful gases when processed.Fume Emission:
During large-scale engraving, unpleasant gases may be released, so proper ventilation and protective masks are recommended for operators.

Performance and Cost Analysis
Processing Cycle: Short and efficient
Production Cost: Relatively low
Material Compatibility: Applicable to nearly all materials
Common Use Cases: Product marking, decorative engraving, artistic designs
Processing Speed: Fast
Engraving Quality: Highly detailed and permanently preserved
Conclusion
Laser engraving technology, with its precision, flexibility, and adaptability, plays an essential role in both industrial manufacturing and artistic creation. As laser technology continues to evolve, its applications are expanding into more industries and design fields, making it one of the most versatile and efficient processing methods today.





