In industrial production, laser marking machines have become an essential tool for product identification, traceability, and branding. However, not all machines are suitable for every type of material. Choosing the right laser marking machine depends on several factors — including the material to be marked, the size of the workpiece, and the desired marking effect.
This guide explains how to select the right laser marking machine for your production needs.
01. Determine the Material to Be Marked
Laser marking machines are mainly divided into three types according to their laser sources: Fiber Laser Marking Machine, CO₂ Laser Marking Machine, and UV Laser Marking Machine.
Each type has a different wavelength and power level, which determine the range of materials it can process effectively.
Fiber Laser Marking Machine
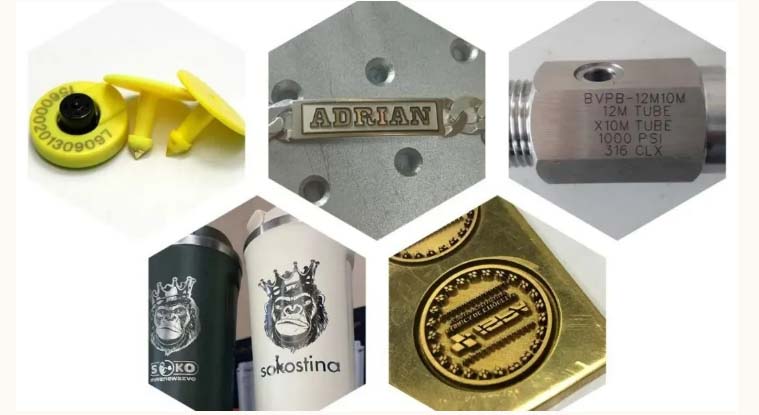
The fiber laser marking machine operates at a wavelength of 1064 nm and is suitable for most metal materials and some non-metal materials such as plastics and hard polymers.
It is widely used for marking stainless steel, aluminum, copper, gold, and other metals, as well as certain nonmetals like leather, fabric, and coated surfaces.
Fiber laser marking machines typically come in different power options — 20W, 30W, 50W, 70W, 100W, and 120W.
20W is suitable for most standard marking tasks, providing clean and clear results.
30W and above are used for deeper engraving or high-efficiency tasks such as VIN code engraving on car parts, engine components, metal nameplates, and industrial pipes.
The optimal power depends on the material and required depth — sometimes lower power gives a better visual effect, while higher power is ideal for deep, fast, or high-volume marking.

Advantages:
Excellent beam quality and high marking precision
Fast marking speed and no consumables
Long service life (over 100,000 hours)

CO₂ Laser Marking Machine
The CO₂ laser marking machine operates at a wavelength of 10.6 μm, making it ideal for non-metallic materials such as paper, leather, wood, plastic, glass, acrylic, rubber, ceramics, and stone.
Available powers include 10W, 30W, 50W, 60W, 100W, 150W, and up to 275W, depending on the required marking depth and production speed.
For instance:
10W–30W is suitable for light engraving and packaging codes.
50W–100W can handle deeper marking or cutting of organic materials like wood or acrylic.
Because different materials react differently to CO₂ laser energy, it’s strongly recommended to test samples before purchasing. Many suppliers offer free test marking to help you find the optimal configuration.

Advantages:
Perfect for non-metal materials
High marking speed and smooth edges
Widely used in packaging, crafts, wood, and textiles

UV Laser Marking Machine
The UV laser marking machine has a wavelength of 355 nm, and it is designed for ultra-fine marking and micro-processing.
Due to its very short wavelength and high photon energy, it causes minimal heat-affected zones, making it perfect for delicate materials such as glass, ceramics, silicon wafers, medical packaging, and transparent plastics.
Common power levels include 3W, 5W, 10W, and 15W.
3W–5W models are most widely used in industrial applications, offering a good balance between precision and cost.
10W–15W models are mainly used for micro-cutting, drilling, and semiconductor processing where ultra-high precision is required.

Advantages:
Ideal for micro-scale and high-precision marking
Non-contact process with minimal heat impact
Excellent results on transparent and fragile materials

02. Consider the Size of the Workpiece
Once you’ve determined the right type of laser marking machine based on your material, the next step is to select a suitable working area (marking field size).
Many users assume that a larger working area is always better, but that’s not true.
A larger marking field usually means:
Higher cost, due to a larger galvo scanner and lens.
Potential beam instability at the edges if the optical design is not high-quality, leading to inconsistent marking depth or brightness.
Tip: Choose a marking field size that just fits your product — it ensures stable performance, better focus accuracy, and more uniform marking results.
03. Match the Machine to Your Specific Processing Needs
Even within laser marking applications, there are various processing modes such as:
Flat marking (for 2D surfaces)
3D or curved surface marking
Static (fixed) marking
Flying marking (on conveyor lines)
Line engraving or surface texturing
Before purchasing a laser marking machine, it’s crucial to clearly define your application requirements — including product type, production speed, marking depth, and integration needs.
Providing detailed information to the supplier helps them recommend the most suitable configuration for your process.
Final Advice
Choosing the right laser marking machine is about matching wavelength, power, and optics to your specific material and production requirements.
If your goal is high-speed metal marking, a fiber laser is your best choice.
If you’re marking non-metallic or organic materials, a CO₂ laser will perform better.
And for ultra-fine or delicate applications, the UV laser delivers unmatched precision.
By understanding your materials and process needs — and working with a professional supplier who offers test marking — you can ensure that the laser marking machine you invest in will deliver long-term stability, efficiency, and exceptional results.