Overall View: The Market Is Taking Off
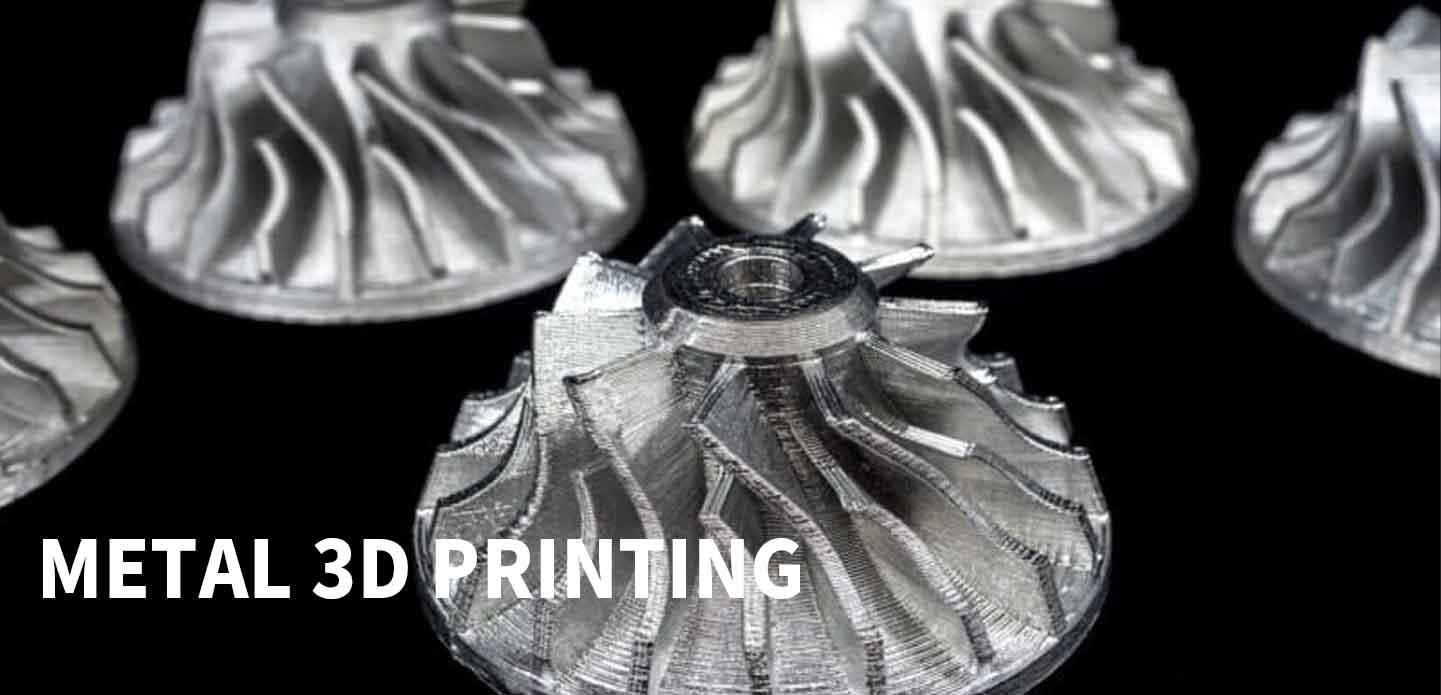
This year, many smartphone manufacturers have launched models containing titanium alloy components. Most of these parts are produced through metal 3D printing. 3D printing can be divided into metal and non-metal categories — today’s focus is on metal.
01. Basic Overview
In the field of metal 3D printing, there are two main categories: industrial-grade and desktop-grade.
Industrial-grade equipment is expensive and mainly used for processing large-sized products.
Desktop-grade equipment targets individual consumers and represents the entry-level stage of additive manufacturing technology.
There are many types of metal printing technologies. The mainstream ones include:
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS)
Selective Laser Melting (SLM)
Electron Beam Melting (EBM)
Laser Engineered Net Shaping (LENS)
Among these, SLM offers a relatively high cost-performance ratio. It provides high density, high strength, high precision, and high material utilization, while maintaining a lower cost than EBM and demonstrating mature technological development. Thus, SLM is currently the mainstream solution in metal 3D printing.
Other technologies include liquid metal additive manufacturing, electrochemical deposition, cold spray metal printing, and metal material extrusion, among others.
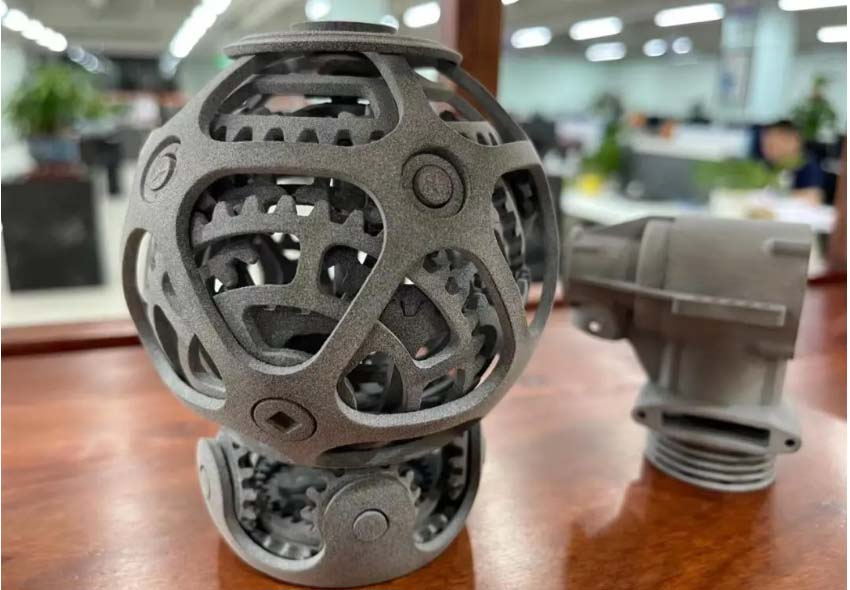

02. Industry Chain
In the metal 3D printing industry, equipment occupies the dominant position in the value chain.
The main components of a 3D printer include galvanometers, lasers, splines, reducers, servo motors, and metal powders. Among them, optical and thermal components (mainly lasers and galvanometers) account for a large proportion of the equipment cost.
The laser processing system is the most expensive part. Metal 3D printing forms final parts by melting metal powder through focused laser irradiation. This laser processing system integrates the laser source, CNC control system, optical components, mechanical structure, and electrical control units.
The control system acts as the “brain” of the entire laser processing system, coordinating all parts for precise operation.
From a technical perspective, laser processing control systems are divided into two major categories:
Galvanometer control systems, focusing on high precision, ultra-fast, and small-format operations.
Servo control systems, focusing on high power applications.
A galvanometer is composed of an optical scanning head, an electronic driver amplifier, and reflective mirrors. It is primarily used in surface processing, engraving, cleaning, welding, and additive manufacturing scenarios in combination with a galvanometer control system.
Application Fields
Metal 3D printing is widely used.
Desktop-grade printers are mostly applied in education, research, and artistic model production, with markets mainly overseas.
Industrial-grade printers dominate the metal 3D printing market, serving sectors such as automotive, defense and aerospace, and machinery manufacturing.
In aerospace, metal 3D printing is used for unmanned aerial vehicle structures, special components, turbine blades, windshield frames, and swirlers — accounting for more than half of the domestic market share.
In automotive manufacturing, it enables prototype fabrication and mold development, producing complex parts, achieving tool-less development, accelerating iteration, and supporting small-batch customized tools, thereby reducing costs and shortening time-to-market. This accounts for about a quarter of the market.
After overcoming challenges in titanium alloy printing, metal 3D printing is now expected to see broader adoption in consumer electronics.
In 2023, major smartphone brands launched products using titanium alloy components. One of them released the world’s first Android smartphone featuring a titanium frame, and another applied titanium alloy 3D printing to the hinge structure of its foldable device — marking the first large-scale application of 3D printing in mobile phones. Wearable device manufacturers have also announced plans to explore titanium alloy 3D printing for structural components.
03. Development Trends
In terms of components, core parts such as lasers and high-end galvanometers are still largely dependent on imports. Although many domestic manufacturers have entered this field and achieved progress in small- and medium-size systems, large-format industrial metal 3D printers still rely mainly on foreign products.
The galvanometer sector remains relatively weak. The high-end market is dominated by foreign suppliers, while domestic manufacturers mostly focus on mid- to low-end applications, leaving a noticeable performance gap.
Once both lasers and galvanometers can be domestically produced and matched effectively, the metal 3D printing system market will gain much more room for expansion.
Technologically, the gap between domestic and foreign metal 3D printing capabilities is narrowing. For example, China mastered titanium alloy structural component laser forming as early as 2013, becoming the second country in the world to achieve this after the United States.
Globally, U.S. enterprises tend to focus more on non-metal materials, while European players emphasize metal printing. The overall technological roadmap for metal 3D printing is stabilizing. Established companies have strong customer bases, high brand recognition, and long-term client relationships, making their positions relatively solid. For emerging firms, it is difficult to gain a competitive edge through new technologies alone.
04. Key Insights
The domestic metal 3D printing equipment market is fragmented, with several leading players and many followers. Under rapid industry growth, small and medium-sized enterprises have certain late-mover advantages.
Many industrial 3D printing patents have expired, lowering entry barriers and costs. While the mid- to low-end market expands rapidly, competition has become increasingly intense.
The consumer electronics market is opening up. As titanium alloy parts become cheaper than traditional CNC machining, the metal 3D printing equipment market is poised for expansion.
In the past, due to low price sensitivity among downstream users, the need for localization of core components was not urgent. However, current domestic lasers and galvanometers can already meet production requirements, and some performance gaps can be compensated through intelligent software algorithms. With the rapid growth of the 3C manufacturing equipment market, cost sensitivity is increasing, and localization of key components — especially lasers and galvanometers, which account for the largest share of equipment cost — will become a major trend in the future.
Contact us for the latest solutions.