
Introduction: The Rise of the 3D Laser Printer
In recent years, the 3D laser printer has become a game-changer in various industries—from aerospace to healthcare and automotive. Unlike traditional 3D printers, a 3D laser printer uses high-powered lasers to fuse, solidify, or cure materials with remarkable precision. Among the most commonly used technologies are SLM 3D printers, SLS 3D systems, and SLA machines, each offering unique advantages depending on the application.
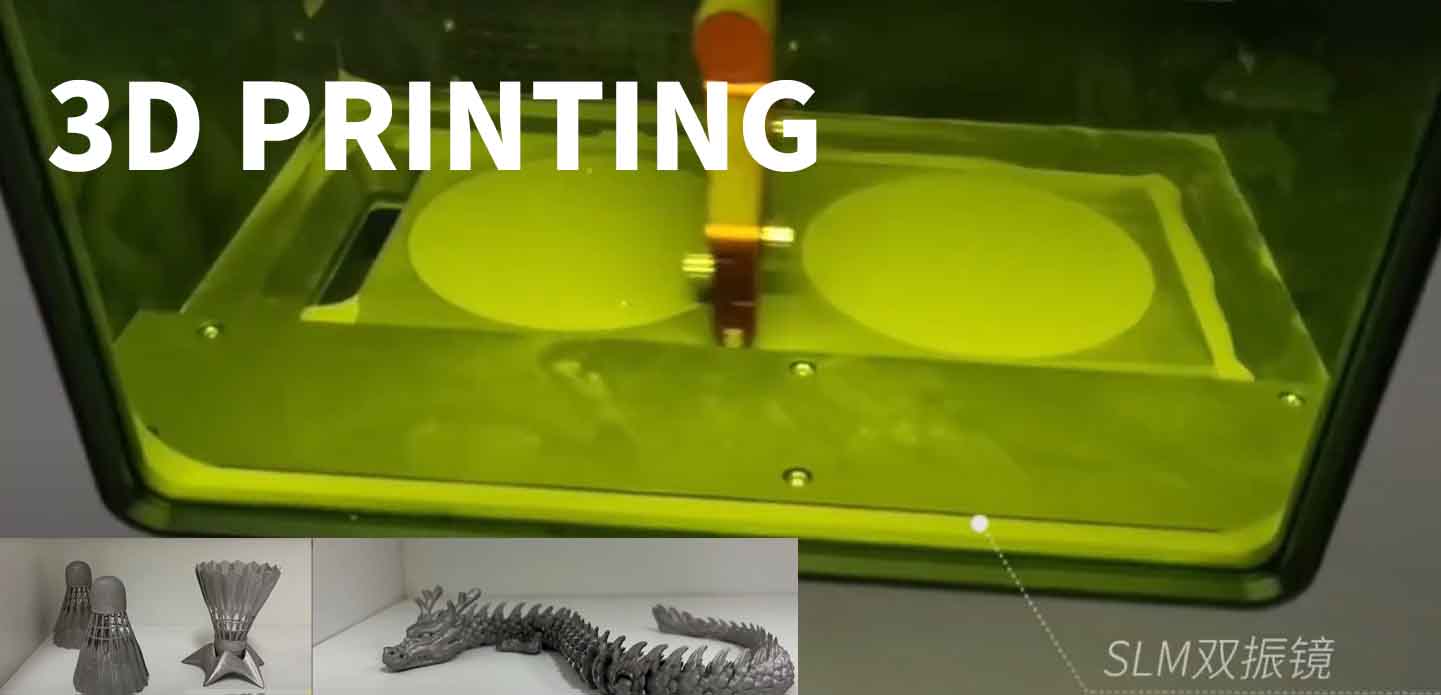
SLM 3D Printer: Metal Additive Manufacturing at Its Finest
SLM (Selective Laser Melting) 3D printers are a subset of powder bed fusion technology. These machines use a high-powered laser to fully melt and fuse metal powder layer by layer, creating incredibly strong and dense parts.
Applications: Aerospace, dental implants, industrial tooling
Materials: Titanium, aluminum, stainless steel
Advantages: High strength, complex geometries, direct metal production
With an SLM 3D printer, manufacturers can produce end-use metal parts that are both lightweight and durable—ideal for applications requiring mechanical performance and weight reduction.
SLS 3D Printing: Versatile, Functional Polymer Parts
SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) is another powder bed fusion process but typically used for nylon and thermoplastics. An SLS 3D printer uses a CO₂ laser to sinter powdered polymer without the need for support structures.
Applications: Prototyping, custom enclosures, automotive parts
Materials: Nylon, TPU, polyamide
Advantages: High accuracy, no support structures, functional prototypes
Unlike other methods, SLS 3D technology is well-suited for producing strong, flexible parts quickly and cost-effectively, making it a preferred choice for rapid prototyping and small-batch production.
SLA Machine: Precision and Detail with Photopolymer Resin
SLA (Stereolithography Apparatus) is one of the earliest 3D printing technologies. An SLA machine uses an ultraviolet laser to cure a liquid photopolymer resin layer by layer, producing parts with exceptional surface finish and intricate detail.
Applications: Dental models, jewelry, miniature components
Materials: Photopolymer resin
Advantages: Ultra-high resolution, smooth finish, excellent detail
For industries requiring intricate designs and smooth surfaces, an SLA machine is the go-to solution, especially in jewelry casting, medical modeling, and consumer electronics prototyping.

Comparing SLM, SLS, and SLA: Which 3D Laser Printer Fits Your Needs?
| Feature | SLM 3D Printer | SLS 3D Printer | SLA Machine |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material | Metal powders | Polymer powders | Photopolymer resin |
| Application Focus | End-use metal parts | Functional prototypes | Detailed models |
| Support Structures | Required | Not required | Required |
| Surface Finish | Moderate | Rough to moderate | Excellent |
| Cost Level | High | Medium | Lower |
Why Invest in a 3D Laser Printer Today?
As businesses seek faster product development cycles and customizable solutions, 3D laser printers offer an ideal path forward. Whether you’re working with SLM 3D printers for metal components, using SLS 3D printers for functional polymer parts, or leveraging SLA machines for detailed prototyping, laser-based 3D printing provides the efficiency and precision required in today’s market.
Conclusion: 3D Laser Printing Is Shaping the Next Industrial Revolution
The future of manufacturing is here. With powerful 3D laser printers, businesses can push the boundaries of what’s possible in design, customization, and production. Whether you choose an SLM 3D printer, explore the flexibility of SLS 3D, or rely on the fine detail of an SLA machine, adopting these technologies can be your next strategic move toward smarter manufacturing.
Call to Action
Looking for a reliable 3D laser printer supplier? We offer high-performance SLM, SLS, and SLA machines tailored to your production needs. Contact us today to learn more.







