Understanding the Basics of Fiber Laser and CO2 Laser
In the world of laser cutting and engraving, two popular technologies dominate the market: fiber laser and CO2 laser. Each of these laser systems has distinct characteristics, applications, and advantages. Choosing between a fiber laser and a CO2 laser depends on your specific needs, materials, and operational goals.
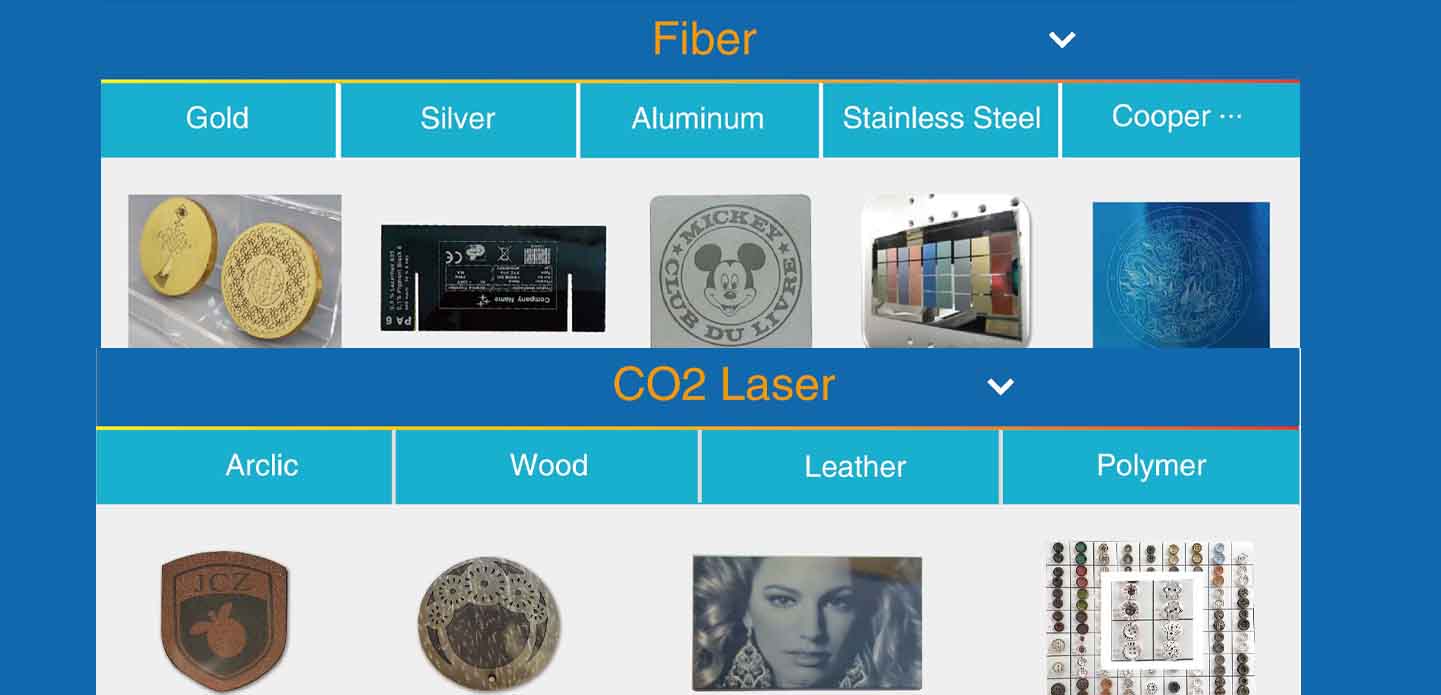
What is a Fiber Laser?
A fiber laser uses a solid-state laser source where the laser beam is generated by diodes and transmitted through a fiber optic cable. This technology is known for its high energy efficiency, low maintenance requirements, and superior beam quality. Fiber lasers are particularly effective for marking, engraving, and cutting metals like stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and copper.
Key Advantages of Fiber Laser:
High precision and beam focus
Faster marking and cutting speed
Long operational life (typically 100,000 hours)
Low cost of ownership due to minimal maintenance
Ideal for metal materials
Because of these advantages, fiber laser machines are widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and jewelry manufacturing.

What is a CO2 Laser?
A CO2 laser is a gas laser that uses a mixture of carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and helium to produce an infrared laser beam. This type of laser is especially efficient when processing non-metallic materials such as wood, acrylic, glass, leather, textiles, and some plastics. CO2 lasers have been around longer and are commonly found in signage and craft industries.
Key Advantages of CO2 Laser:
Excellent for non-metal materials
Lower upfront machine cost
Smooth cutting edges on organic materials
Versatile for artistic and design applications
While CO2 laser systems are not as efficient for metal cutting as fiber lasers, they remain the best option for engraving and cutting non-metals.

Fiber Laser vs CO2 Laser: Head-to-Head Comparison
| Feature | Fiber Laser | CO2 Laser |
|---|---|---|
| Beam Wavelength | ~1064 nm (Near-Infrared) | ~10.6 µm (Far-Infrared) |
| Material Compatibility | Metals (ideal) | Non-metals (ideal) |
| Cutting Speed | Faster for metals | Slower for metals, good for non-metals |
| Maintenance | Low | Higher (due to glass tubes, mirrors) |
| Operating Costs | Lower (more energy efficient) | Higher (requires more power) |
| Machine Cost | Higher initial cost | More affordable for beginners |
Depending on your target materials and production volume, you can decide whether a fiber laser or CO2 laser is the better fit.
Which Laser is Right for You?
If your primary focus is cutting or engraving metals, the clear winner is the fiber laser. Its high speed, precision, and efficiency make it ideal for industrial use. However, if you’re working with non-metallic materials like wood, acrylic, or leather, a CO2 laser will provide cleaner results and more flexibility.
For businesses that need to handle both metals and non-metals, some manufacturers offer hybrid laser machines or recommend using both systems in parallel.
Conclusion
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer when it comes to choosing between a fiber laser and a CO2 laser. Each has its strengths and best-use scenarios. Whether you’re a hobbyist, a small business owner, or managing industrial production, understanding the differences between fiber laser and CO2 laser technologies will help you make a more informed investment.







