A laser engraving machine, as the name suggests, uses a laser beam to engrave or cut various materials with high precision. It applies thermal energy to vaporize or melt the surface of the material, leaving smooth edges without burrs. Because of its precision and efficiency, it is widely used in industries such as advertising, gifts, packaging, leather, garments, and architectural modeling.
Here are some commonly processed materials and daily precautions for using a laser engraving machine.
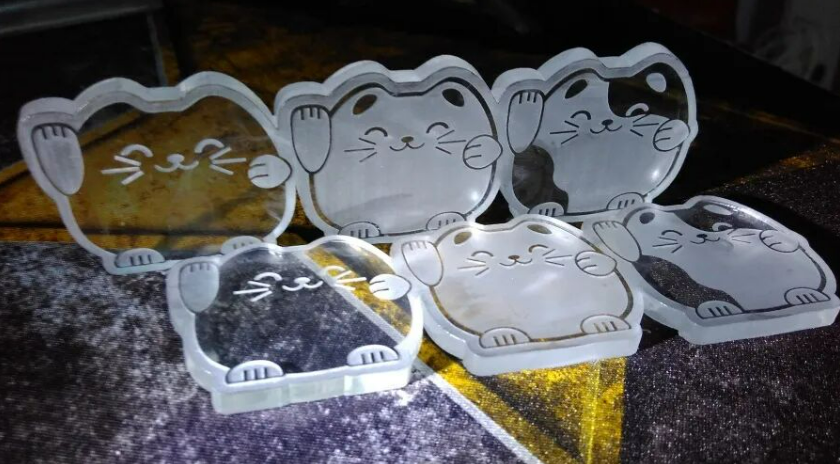
Acrylic (PMMA)
Acrylic, also known as plexiglass, is widely used in the advertising industry. Whether for full-sheet engraving or cutting, the use of a laser engraving machine offers cost-effective and high-quality results. Typically, the engraving is done in reverse—engraved from the front and viewed from the back—to create a more three-dimensional appearance.
When reverse engraving, the design should first be mirrored, and the engraving speed should be fast with low power. Acrylic is easy to cut, but you should always use an air assist device to improve edge quality. Never leave the machine unattended, as flames may appear during the cutting process.

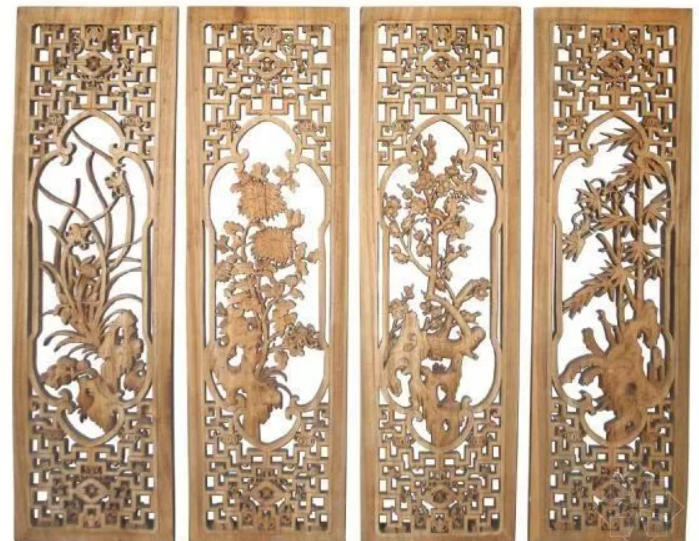
Wood
Wood is one of the easiest materials to engrave and cut with a laser engraving machine. Light-colored woods such as birch, cherry, or maple vaporize well under laser heat, producing fine engraving results. Basswood, one of the most popular materials, is easy to carve and has a smooth texture similar to linden wood. Since its grain is subtle, applying coloring to engraved areas is recommended for a better appearance.
When processing thicker wood panels, ensure proper ventilation or use a smoke purifier to handle the heavy fumes generated.

MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard)
MDF is commonly used for signage backing or wooden bases. It can be engraved by laser machines, but the engraved color tends to be uneven and dark, so post-coloring is often needed. To achieve better contrast and precision, designers often inlay 0.5mm two-color plastic sheets into MDF.
After engraving, use a damp cloth to clean the surface and remove any residue.

Two-Color Plastic Sheet
A two-color plastic sheet consists of two or more layers of contrasting colors. It is specifically designed for laser engraving, offering sharp, clear, and visually appealing results. Standard sizes are 600×1200mm, with some variations at 600×900mm. Laser engraving produces excellent contrast and smooth edges on this material.
Coated Copper Sheet
Generally, pure copper cannot be directly engraved by laser. However, special coated copper sheets have a thin paint layer on the surface that can be vaporized by the laser, exposing the shiny copper beneath. Manufacturers often polish or treat the copper surface before coating, ensuring that engraved areas remain bright and durable.
If the copper is not pre-treated, it is recommended to apply a protective coating after engraving to prevent oxidation and discoloration over time.
Other Applicable Materials
Laser engraving machines are not limited to the materials above. They can also process glass bottles, ceramics, paper, leather, textiles, and fabrics, providing endless design possibilities across different industries.
Common Problems and Troubleshooting
Uneven Bottom Surface
If you find the engraved bottom uneven or dirty, it may be due to excessive speed or incorrect air flow. Adjust the speed and airflow settings accordingly.Improper Focus Lens Selection
Using the wrong focus lens can cause uneven engraving depth or blurry edges. Always select a lens suited for the material thickness.Misaligned Laser Path
Laser engraving depends on accurate reflection through multiple mirrors. If the laser path is not perfectly aligned, cutting precision will decrease. Regularly check and calibrate the optical path.

Final Tips
When encountering issues during operation, inspect the laser path, power supply, and engraving depth carefully. Lower the processing speed to reduce material burn or residue buildup. If the power supply or focus is found to be faulty, replace it immediately. By maintaining proper settings and timely maintenance, you can significantly improve engraving quality and machine lifespan.





